Simply explained, sandstone is sand that has been bonded with rock; you can discover this by closely examining a specimen. Beyond that straightforward description, however, lies an intriguing composition of cement, matrix, and sediment that, when further investigated, Indian Sandstone can offer a wealth of important geologic data.

Basics of Sandstone
Sandstone refers to a sedimentary rock formed from sediment. Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock because the sedimentary particles are bits and parts of rock and minerals. Sandstone is a mid-grained clastic sedimentary rock because it mostly consists of medium-sized sand particles. Sand has a size range of 1/16 millimeter to 2 millimeters. The term “framework grains” describes the individual sand particles that makeup sandstone.
Sandstone may contain both fine and coarse material and is referred to as sandstone, but it contains more than 30% gravel, grains, or cobbles, it is categorized as breccia or conglomerate.
In addition to the sediment particles, sandstone contains two additional types of material: cement and matrix. Cement is the mineral substance that was added later to bond the sediment into rock, whereas matrix refers to the fine-grained material that was present in the sediment together with sand.

Poorly sorted sandstone is characterized by a high matrix content. A wacke is referred to as the case where the matrix makes up more than 10% of rock content. Arenite is a name for a well-formed sandstone with minimal cement and little matrix. Wacke is unclean and arenite is spotless, to put it another way.
You’ll probably note that no specific minerals are mentioned in this talk; only a certain particle size is. In actuality, however, minerals play a significant role in the geologic history of sandstone.
Sandstone Minerals

Rocks formed of carbonate minerals are not considered to be Indian sandstone since the term is technically defined as solely referring to particle size. Sandstone really refers to a silicate-rich rock since these rocks are referred to as limestone and assigned a completely different classification. Calcarenite is a kind of mid-grained clastic carbonate rock, sometimes known as “limestone sandstone.” This distinction is reasonable given that silicate rocks developed from material eroded off continents, whereas limestone is formed in pure ocean water.
Sandstone is often composed almost entirely of quartz because mature continental silt is mostly composed of a few surface minerals. The clastic portion or matrix is coloured and characterized by other minerals, such as clays, feldspar, hematite, ilmenite, mica, and amphibole, as well as minute rock pieces and organic carbon (bitumen).
Arkose is a kind of sandstone that contains a minimum of 25 percent feldspar. Tuff is a kind of sandstone composed of volcanic ash.
Three substances are often used as the cement in sandstone: silica (which is chemically identical to quartz), iron oxide, or calcium carbonate. These may penetrate the matrix and hold it together, or they might fill the empty spaces left by the matrix.
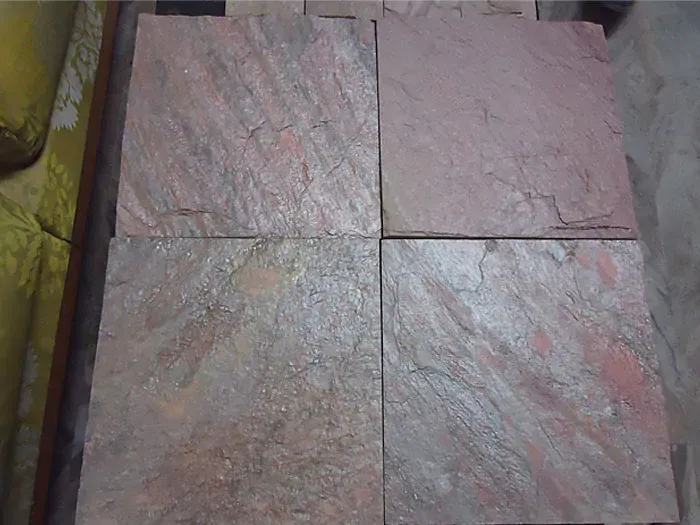
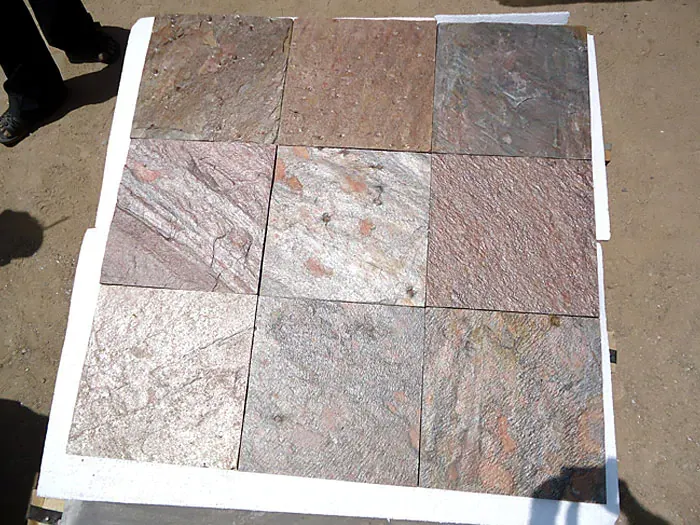
Indian Sandstone can range in color from almost white to almost black, with grey, red, brown, pink, and buff in between, depending on the ratio of matrix to cement.
The Formation of Sandstone
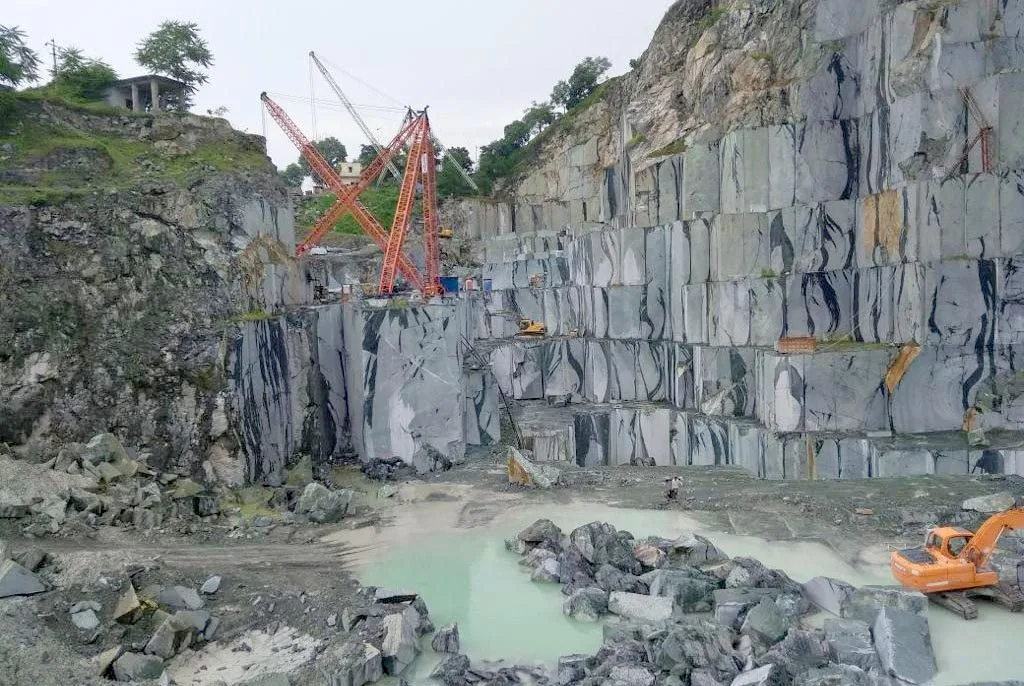
Where sand has been buried, sandstone has formed. Sandstone beds can be left in the geologic data by desert dunes and beaches as well as offshore from river deltas. For instance, the Grand Canyon’s famed red rocks originated in an arid environment. Although the dynamic settings and sand beds occur do not usually promote preservation, fossils can be found in sandstone.
Sandstone contains information about the past in the form of grains of sand:
- Feldspar and lithic grains indicate that the silt is near the mountains where it originated.
- Sandstone may be thoroughly studied to learn more about its origins, or the type of landscape that created the sand.
- The grains’ degree of rounding indicates how far they traveled.
- A frosty surface often indicates that sand was carried by the wind, which indicates a sandy desert environment.
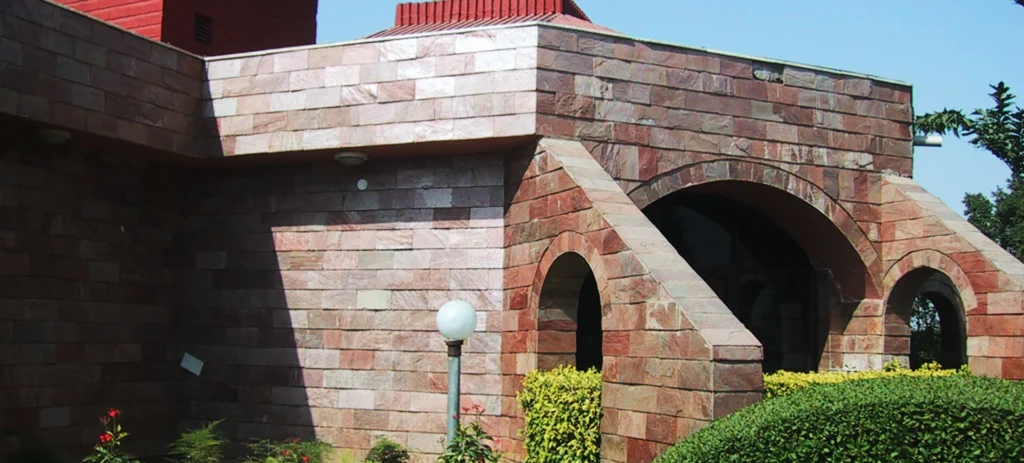
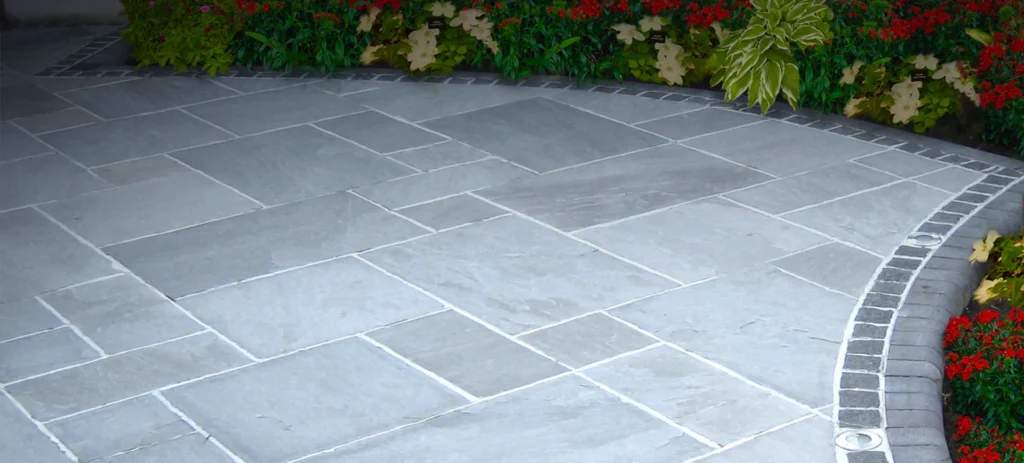
Sandstone has warm hues and lots of character, making it a great choice for landscaping and construction. It may also be rather robust. Flagstones are the primary usage of sandstone mined nowadays. Commercial sandstone is exactly what the geologists claim it is, in contrast to commercial granite.
Some of the popular sandstone variants from India are:

Kandla Grey Sandstone
Kandla Gray Sandstone, also known as Bhilwara Grey Sandstone, is one of the most widely used sandstones in India. Due to its great hardness, this sandstone is frequently used for paving and other architectural uses. This gray-colored natural stone comes in two shades, light grey, and dark grey, and is frequently exported to nations including the USA, UK, Europe, the UAE, and Australia.
This Indian sandstone is available in a variety of treatments, including tumbled, honed, brushed, natural bush hammered, and sandblasted. Both hand-cut and machine-cut edges are available for it.
Camel Dust Sandstone
It is a yellow-colored sandstone that draws attention to surface bands of dark brown tint. The stone is incredibly strong and resistant to many substances, including acids, abrasion, and alkalis. It is frequently employed as a paving stone, pool coping stone, interior and exterior wall, floor, countertop, sink, monument, and decorative stone.
For both residential and commercial building projects, there are several sandstone suppliers in India that offer high-quality camel dust sandstone.


Rainbow Sandstone
The warmth and beauty of real stone are added to your environment by this high-end Indian natural stone. The vibrant swirls and patterns of colour on each paving stone make it highly eye-catching. Of all the paving stones in our inventory, the Rainbow Indian sandstone is the most unusual.
Bright orange and purple swirls can be seen all over it. These hues will brighten any patio and add natural beauty to your environment. On the surface, it was simple to understand why it was so well-liked.